Presupuestos de la unión Europea 2021
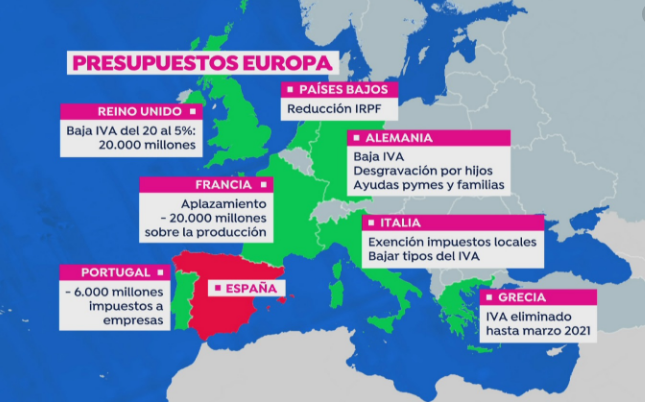
Comparativa de los impuestos en la Unión Europea
| Country | Corporate tax | Corporate tax | maximum income rate | Maximum income tax rate | Standard VAT rate |
| Albania | 0,15 | 0,15 | 0,23 | 0,23 | 0,2 |
| Andorra | 0,1 | 0,1 | 0,1 | 0,1 | 4.5% |
| Austria | 0,25 | 0,25 | 0,55 | 0,55 | 20% (Reduced rates 10% + 13%) |
| Belarus | 0,18 | 0,18 | 0,15 | 0,15 | 0,2 |
| Belgium | 0,25 | 29% (25% from 2020. For SME’s 20% from 2018 on the first €100,000 profit) | 0,5 | 50% (excluding 13.07% social security paid by the employee and also excluding 32% social security paid by the employer) | 21% (Reduced rates of 6% and 12%) |
| Bosnia and Herzegovina | 0,1 | 0,1 | 0,1 | 0,1 | 0,17 |
| Bulgaria | 0,1 | 0,1 | 0,1 | 10% (additional 12.9% by the employee for social security contributions, i.e. health insurance, pension and unemployment fund); and additional 17.9% by the employer for various social security contributions) | 20% (Reduced rates 9%) |
| Croatia | 0,18 | 18% (Reduced rate 12% for small business) | 0,4 | 40% (excluding 35.2% total sum of insurances levied on income) | 25% (Reduced rates 13% + 5%)(Reduced rates 9%) |
| Cyprus | 0,125 | 12.5% | 0,35 | 0,35 | 19% (Reduced rates 5% + 9%)(Reduced rates 9%) |
| Czech Republic | 0,19 | 0,19 | 53.5% (15% income tax + 6.5% by employee + 25% by employer (2.3% healthcare + 21.5% social security + 1.2% state policy of employment) + 7% solidarity contribution (assuming income is above 1 277 328 CZK per year)) | 21% (reduced rates of 15% and 10%) | |
| Denmark | 0,22 | 0,22 | 0,52 | 51.95% (including 8% social security paid by the employee but excluding 0.42–1.48% church tax imposed on members of the national Church of Denmark) | 25% (reduced rate 0% on transportation of passengers and newspapers normally published at a rate of more than one issue per month) |
| Estonia | 0 | 20% CIT on distributed profit. 14% on regular distribution. 0% on undistributed profits. | 0,2 | 20% (+ 2.4% of unemployment insurance tax, 0.8% paid by employer, 1.6% paid by employee and 33% social security which is paid before gross wage by employer) around 57,8% in total | 20% (reduced rate 9%) |
| Finland | 0,2 | 0,2 | 0,67 | 25% to 67% depending on the net income and municipality, including 7.8% social insurance fees, employee unemplayment payment and employer unemployment payment, which is on average 18% (2018). | 24% (reduced rate of 14% for groceries and restaurants, 10% for books, medicine, transport of passengers and some others) |
| France | 0,3 | 30% (including social contributions) after 2018 (‘PFU’), before: 33.3% (36.6% above €3.5M, 15% below €38k) | 0,45 | 49% (45% +4% for annual incomes above €250,000 for single taxpayers or above €500,000 for married couples) [20] + social security and social contribution taxes at various rates, for example 17,2 % for capital gains, interests and dividends. | 20% (reduced rate of 10%, 5.5%, 2.1% and 0% for specific cases like some food, transportation, cultural goods, etc.) |
| Germany | 0,228 | 22.825% (few small villages) to 32.925% (in Munich) depending on the municipality. This includes the 15% CIT, 5.5% solidarity surcharge plus the trade tax payable to the municipality. | 0,48 | 47.475% which includes 45% income tax and 5.5% solidarity surcharge based on the total tax bill for incomes above €256,304. The entry tax rate is 14% for incomes exceeding the basic annual threshold of €9,000. | 19% (reduced rate of 7% applies e.g. on sales of certain foods, books and magazines, flowers and transports) |
| Georgia | 0,15 | 0,15 | 0,2 | 0,2 | 0,18 |
| Greece | 0,28 | 0,28 | 0,66 | 65.67% (45% for >€40,000+ 7.5% Solidarity Tax for >€40000)+(26.95% Social Security for employees or up to 47.95% for private professionals) | 24% (Reduced rates 13% and 5%) |
| Hungary | 0,09 | 0,09 | 0,43 | Total: 43.16% | 27% (Reduced rates 18% and 5%) |
| 0 | 0,33 | Employee: 33.5% of gross salary (Employee expenses altogether of gross salary without children: 15% Income Tax (flat), Social Security: 10% Pension, 3% in cash + 4% in kind Health Care, 1.5% Labor Market contributions)[22] | |||
| 0 | Employer: 17% in addition to gross salary (15.5% Social Tax, 1.5% Training Fund Contribution)[23] | ||||
| Iceland | 0,2 | 0,2 | 0,37 | 36.94% from 0 – 834.707 and 46.24% over 834.707 kr (2017) | 24% (12% reduced rate) |
| Ireland | 12.5% for trading income | 12.5% for trading income | 0,4 | 40% over €34,550 for single, €42,800 for married taxpayers.Plus USC(Universal Social Charge)4.5% on income up to €50,170 and 8% on balance. Social insurance 4% | 23% |
| 0,25 | 25% for non-trading income | ||||
| Isle of Man | 0 | 0 | 0,13 | 20% plus national insurance of under 12.8% | Same as United Kingdom (see below) |
| Italy | 0,279 | 27.9% (24% plus 3.9% municipal) | 0,46 | 45.83% (43% income tax + 2.03% regional income tax + 0.8% municipal income tax) | 22% (Reduced rates 10%, 5%, 4%) |
| Latvia | 0 | 20% CIT on distributed profit. 0% on undistributed profits. 15% on small businesses | 0,2 | 20%(income tax) 35.09%(social insurance) Total up to 55.09% | 21% (reduced rates 12% and 0%) |
| Liechtenstein | 12.5% | 12.5% | 0,28 | 28% (max. 8% national and 20% municipal income tax) plus 4% of the taxpayer’s net worth is subject to the same rate as wealth tax. 0% on capital gains. | 8% / 2.5% (till 31.12.2017) |
| 0 | 7.7% / 2.5% (from 01.01.2018) | ||||
| Lithuania | 0,15 | 15% (5% for small businesses) | 0,44 | 44.27% (effective tax rates: 34.27% social insurance (nominally it is 1.77% payable by employer + 19.5% payable by employee + from 1.8% to 3% optional accumulation of pence), 20% income | 21% (Reduced rates 5%, 9%) |
| Luxembourg | 0,2495 | 24.94% (commercial activity); 5.718% on intellectual property income, royalties. | 0,43 | 43.6% (40% income tax + 9% solidarity surcharge calculated on the income tax) | 17% (Reduced rates 3%, 8%, 14%) |
| Republic of North Macedonia | 0,1 | 0,1 | 0,37 | 37% [39] (includes income tax 10%, mandatory state pension 18%, mandatory public health insurance 7.3%, mandatory unemployment insurance 1.2%, mandatory personal injury insurance 0.5%) | 0,18 |
| Malta | 0,1 | 35% (6/7 or 5/7 tax refunds gives an effective rate of 5% or 10% for most companies | 0,35 | 35% (additional 10% by the employee for social security contributions, i.e. health insurance, pension and education); and additional 10% by the employer for various social security contributions) | 18% (Reduced rates 5%, 7% and 0% for life necessities – groceries, water, prescription medications, medical equipment and supplies, public transport, children’s education fees) |
| Monaco | 0 | 0% (>75% revenue within Monaco) or 33.33% | |||
| Montenegro | 0,09 | 0,09 | 0,13 | 12.65% (11% income tax + 15% of the income tax bill to the municipality) | 0,21 |
| Netherlands | 0,165 | 25% above €200,000 of profit and otherwise 16.5% | 0,49 | 49.5% (excluding income dependent bracket discount for incomes up to €98.604) | 21% (reduced rate of 9% and 0% for some goods and services) |
| Norway | 0,22 | 0,22 | 0,46 | 46.4% (53.0% including 14.1% social security contribution by employer. All taxes include 8.2% pension fund payments). | 25% (reduced rate of 15% for groceries, and 10% for transport and culture.) |
| Poland | 0,19 | 19% (Reduced rate 9% for small business since 01.01.2019) | 0,17 | 17% up to 85 528 zł (from 1.10.2019) | 23% (reduced rates of 5% and 8%) |
| 0 | 0,32 | 32% above 85 528 zł (~20 000 euro) | |||
| Portugal | 0,24 | 21% + 3 to 9% depending on profit | 0,48 | 48% + 5% solidarity surcharge + 11% social security (paid by the employee) + 23,75% (social security paid by the company) | 23% (reduced rates 13% and 6%) |
| Romania | 0,01 | Revenue <€1m: 1% of all sales | 0,41 | Employee: 41.5% [10% income tax (out of gross minus pension & health deductions), 25% pension contribution (out of gross), 10% health contribution (out of gross)] – Gross incomes below RON 3,600 benefit from personal deductions of up to RON 1,310 from taxable income. | 19% (reduced rates of 9% and 5%) |
| Revenue >€1m: 16% on profit | Revenue >€1m: 16% on profit | 0,03 | Employer: 2.25% (compulsory work insurance) | ||
| Russia | 0,2 | 0,2 | 0,43 | 43% (13.0% income tax, 22.0% mandatory pension fund contribution, 2.9% unemployment insurance, 5.1% mandatory universal health insurance) | 0,2 |
| Serbia | 0,15 | 0,15 | 0,52 | 52% (capital gains tax 15%, standard income tax rate 10%, additional contributions by employee: 13% state pension fund, 6.5% state health fund, 0.5% unemployment fund; additional contributions by employer: 11% state pension fund, 6.5% state health fund, 0.5% unemployment; maximum contributions capped (amount changing monthly); additional tax for higher salaries (after 3 times average salary additional 10%, after 6 times average salary additional 15%)) | 20% (10% reduced rate) |
| Slovakia | 0,21 | 21% | 0,5 | 50% (income tax 19% + 25% for the part of annual income greater than €35,022.31; additional contributions at 4% mandatory health insurance by employee and 10% by employer, 9.4% Social Security by employee and 25.2% by employer) | 20% (10% reduced rate) |
| Slovenia | 0,19 | 0,19 | 0,5 | 0,5 | 22% (reduced rate 9.5%) – from 1 July 2013 |
| Spain | 0,25 | 0,25 | 0,45 | 45% maximum Income tax rate. Not including employee contribution of 6.35% Social Security tax, 4.7% pension contribution tax, 1.55% unemployment tax, 0.1% worker training tax. Not including employer contribution of 23.6% Social security tax, 5.5% unemployment tax, 3.5% (or more) workers comp tax, worker training tax .06%, 0.2% FOGASA tax (employment tax in case of company bankruptcy). | 21% (reduced rates 10% and 4%) |
| 4% in the Canary Islands | 4% in the Canary Islands | ||||
| Sweden | 0,22 | 22% (21.4% 2019, 20.6% 2021) | 0,55 | 55.5% including social security paid by employer | 25% (reduced rates 12% and 6%) |
| Switzerland | 16.55% | 16.55% | 0,22 | 22.5% (Kanton Zug, Gemeinde Walchwil) to 46% (Kanton Geneve), average rate 34%. These taxes do not include social security that is private and not income based (e. ) | 8% / 2.5% (till 31.12.2017) |
| 0 | 7.7% / 2.5% (from 01.01.2018)[35] | ||||
| Ukraine | 0,18 | 0,18 | 0,17 | 0,17 | 0,2 |
| United Kingdom | 0,19 | 0,19 | 0,47 | 47% (45% income tax + 2% NI) – theoretically, NI could reach 12%, but in practice it’s never combined with the higher income tax rate | 20% (reduced rate of 5% for home energy and renovations, 0% for life necessities – groceries, water, prescription medications, medical equipment and supplies, public transport, children’s clothing, books and periodicals) |
| 0 | For earnings between £100,000 – £125,000 employees pay the 40% higher rate tax + removal of tax free personal allowance + 2% NI | ||||
| 0 | 0,45 | 45% (additional rate) income tax on annual income above £150,000, 40% (higher rate) between £43,001 and £150,000, 20% (basic rate) between £0 and £43,000. There is also a National Insurance levy between 2% and 13.8% for employees and self-employed individuals but capital gains and dividend income is not subject to NI. The first £12,500 is tax-free if your annual income is below £100,000. | |||
| 0 | 0,2 | Capital gains is taxed at 10% (or 18% on residential property) for basic rate taxpayers and 20% (or 28% on residential property) for higher and additional rate taxpayers. Dividend income from UK companies is taxed at 7.5% for basic rate taxpayers, 32.5% for higher rate taxpayers and 38.1% for additional rate taxpayers. |
Laisser un commentaire
Participez-vous à la discussion?N'hésitez pas à contribuer!